The Future of Living: Smart Architecture Trends Shaping 2030
Architecture is evolving faster than ever before, driven by technological breakthroughs, environmental urgency, and changing lifestyle demands. By 2030, smart architecture trends will redefine not only how our homes look, but also how they function, conserve energy, and improve our daily lives in ways we’re just beginning to imagine.
The convergence of artificial intelligence, sustainable materials, and innovative construction methods is creating a perfect storm of architectural revolution. Future housing 2030 won’t just be for the wealthy—many of these innovations promise to make quality housing more affordable, efficient, and environmentally friendly than ever before.


1. Net-Zero and Carbon-Negative Homes
The most crucial architectural shift isn’t just about reducing energy consumption—it’s about creating buildings that actively remove carbon from the atmosphere while providing superior living experiences.
Carbon-negative homes go beyond net-zero by sequestering more carbon than they emit throughout their entire lifecycle. Revolutionary bio-based materials like hempcrete actually absorb CO2 as they cure and continue capturing carbon throughout the building’s life. These homes feature sophisticated AI-powered energy management systems that optimize solar panels, battery storage, and geothermal heating while often generating surplus energy for the grid.
2. 3D Printed Construction
3D printed homes are transitioning from experimental curiosities to mainstream construction solutions, with the global market valued at $13.84 billion in 2021 and expected to expand at a 20.8% annual growth rate through 2030.
A complete house structure can be 3D printed in 24-48 hours, dramatically reducing labor costs and construction timelines without compromising quality. This technology offers unprecedented design freedom, allowing curved walls and complex geometries impossible with conventional construction.
Modern 3D printing utilizes locally sourced materials, including mixtures of local soil, chopped straw, and rice husks from waste production. This precision eliminates the 30-40% material waste typical in traditional construction while reducing transportation costs and environmental impact.
3. Smart Glass and Adaptive Materials
Buildings of 2030 will feature materials that respond intelligently to environmental conditions. Smart glass automatically adjusts transparency, insulation, and color based on weather, time of day, and occupant preferences, eliminating traditional blinds while providing perfect privacy and light control.
These dynamic materials can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 40% by becoming more insulating during cold weather and heat-reflective during hot periods. Next-generation versions incorporate displays and communication systems directly into walls, creating surfaces that can show artwork or serve as video screens when needed.
Emerging self-healing materials can repair minor damage automatically using embedded healing agents that activate when cracks occur, extending building lifespans and reducing maintenance requirements.
4. Floating and Amphibious Homes
Climate change and rising sea levels are driving innovation in water-adapted architecture. Amphibious homes remain on dry land during normal conditions but float safely during flood events, automatically rising with water levels while maintaining utility connections.
Floating communities are being designed as artificial reefs that support marine life while providing human habitation. These structures achieve greater energy independence through integrated tidal generators, floating solar arrays, and ocean thermal energy systems, pioneering new models of sustainable community living.
5. Biophilic Architecture
The integration of natural elements into built environments is evolving from aesthetic choice to health necessity. Biophilic design emphasizes the connection between humans and nature to enhance well-being and create calming, restorative environments.
Advanced implementations include complete ecosystems with integrated food production, natural water filtration through constructed wetlands, and climate control through strategic vegetation placement. Buildings increasingly mimic natural forms—termite mound ventilation for cooling, tree-like structures for load distribution, and photosynthesis-inspired energy generation.
Research consistently shows that being in nature lowers stress levels and increases productivity, making biophilic design a practical investment in occupant wellbeing and performance.
6. Modular and Flexible Designs
The future demands adaptable architecture that evolves with changing needs. Modular homes of 2030 feature standardized connection systems allowing rooms to be added, removed, or reconfigured easily. Need a home office? Click in a work module. Kids moved out? Convert their rooms into rental units.
Factory-built modular components achieve higher quality standards than site-built construction while reducing costs and time. Factory construction eliminates weather delays and enables precise integration of smart systems. These buildings are designed for multiple lifecycles, with components that can be upgraded, relocated, or repurposed as needs change.
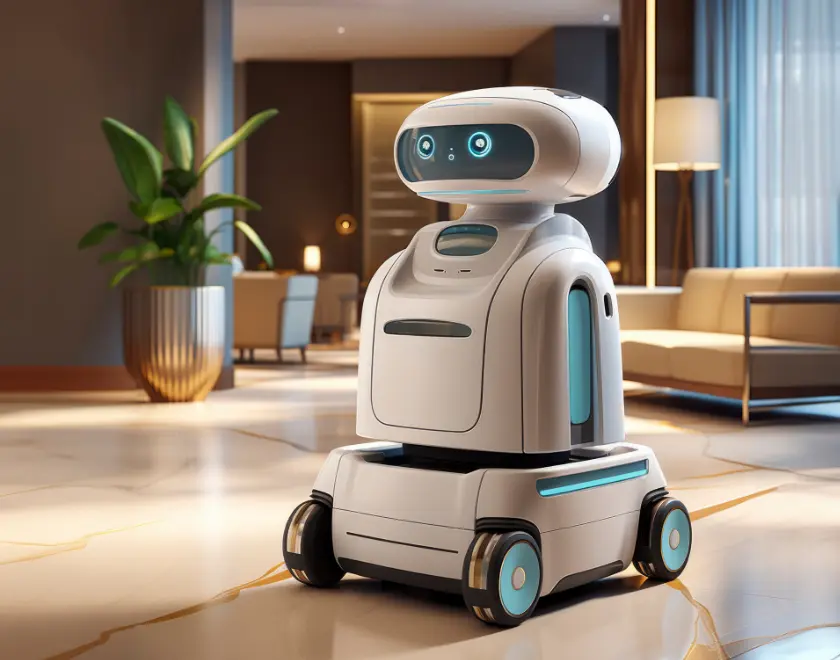
7. AI-Integrated Homes
Artificial Intelligence is predicted to play a significant role in future smart homes, taking automation and efficiency to new heights. By 2030, AI-powered home assistants and automated systems will become standard in newly built homes.
Advanced systems learn occupant patterns and preferences to optimize comfort, energy use, and security automatically. They monitor air quality, detect potential health issues through environmental sensors, and automatically adjust conditions to support occupant wellbeing. Unlike today’s programmable systems, AI homes continuously learn and adapt, understanding seasonal patterns and even adjusting to emotional states detected through voice patterns and movement.
Conclusion
By 2030, smart architecture trends will blur the lines between technology, sustainability, and design, creating living environments that are more responsive, efficient, and harmonious than anything we’ve experienced before. The most exciting aspect is their convergence—imagine a 3D-printed home with carbon-negative materials, AI-optimized energy systems, biophilic living walls, and modular spaces that adapt to your changing life.
Future housing 2030 will be more affordable, sustainable, and responsive than today’s best homes while requiring less maintenance and providing superior living experiences. We’re not just building better houses—we’re designing a more sustainable and harmonious way of living on Earth.
Contact us today to schedule a site visit and experience Enclavar’s thoughtfully designed apartments.
Email : marketing@enclavar.in
Visit: www.enclavar.in